- Domains
- DNS Management
- Content Delivery Network
-
Cloud Containers
- Overview
-
Using Containers
- Creating and Managing
- Connecting to a Container
- Swapping the Image
- Domain Aliases
- Environment Variables
- Protected Environment Variables
- Backing Up
- Automatic Updates
- SSL Support
- Adjusting Execution Time Limits
- Upgrading Apache Image
- Renaming a Container
- Port Management
- Caching
- Cloning/Overwriting
- Restoring a Backup
- Production Mode
- Metrics Dashboard
- Accessing supervisord
- Container Deprecation
- SSH / SFTP Users
- Databases
- Volumes
- Custom Images
-
Technical Guides
- Create a NodeJS Container
- Creating a Service Container
- Working with .NET Core Web Containers
- Working with Node.js Web Containers
- Working with Umbraco Web Containers
- Deploying your application with git
- Python Container
- Enable Country-Level blocking in Cloud Containers
- Working with SQL Server Containers
- Working with the SilverStripe Caching folder
- Profiling a site using Xdebug on Cloud Containers
- Working with SilverStripe Containers
- NGINX Proxy for Service Containers
- Tuning PHP OPcache
- Deploying phpList on SiteHost Cloud Containers
- Deploying Mautic on SiteHost Cloud Containers
- Low Disk Warnings & Upgrades
- Local Development
- Virtual Servers
- Dedicated Servers
- Private Cloud
- Cloud / Shared Hosting
- Email Hosting
- Monitoring & Bandwidth
- Account & Billing
- Developers
- SSL Certificates
NGINX Proxy for Service Containers
Every Cloud Container server comes with an NGINX Proxy built-in, which automatically adapts to any web containers you create. All web traffic on port 80/443 arrives at this container first, which routes the traffic to the correct web container.
In some cases, you might have a service container that you'd like to serve out to the web. Since port 80/443 are already exposed by the built-in NGINX Proxy container, you're not able to expose those directly from your service container, and because it's not a web container, the proxy won't automatically route requests to it.
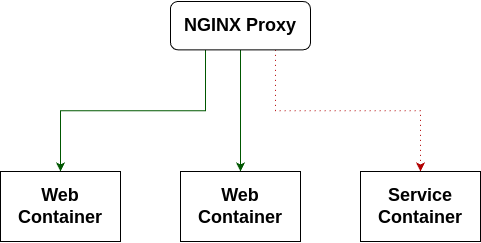
For those standalone services, we offer an NGINX Proxy container which can act as a second-layer reverse proxy for your service container. This additionally allows you to configure the proxy however you'd like - you can use practically any directive that NGINX will allow for a host. Keep in mind, though, that if you're looking to increase timeouts or request size limits you'll need to get in touch with us to apply that upstream as well.
The NGINX Proxy container should have a container name/alias for the domain(s) you want to route, just as a web container would.
So, if your service container's listening on port 8080, you can configure the NGINX Proxy to accept traffic for its hostname and forward it to the upstream container's port 8080, using a config like: